Table of contents:
Introduction
What is an air compressor?
Types of Air Compressors
- Reciprocating Air Compressor
- Rotary Screw Air Compressor
Specialized Tools
- Blowers:- Twin Lobe Roots Blower
- Vacuum Pumps:- Reciprocating Dry Vacuum Pump
- Air Dryers:- Refrigeration Air Dryer
- Boosters:-
- Vacuum Booster
- High-Pressure Air Boosters
Conclusion
You need to know everything about Air compressors, their Types, and how they work.
Introduction

We are RR Enterprises, your one-stop destination for compressed air solutions. Our blog serves as your guide to understanding air compressors, and we'll explore the different types of air compressors, from reciprocating models to rotary screw compressors, as well as specialized tools like vacuum pumps and air dryers. By the end of this blog, you'll be equipped to choose the right equipment for your needs, whether you're a DIY enthusiast or a professional in the industrial landscape.
What is an air compressor?
An air compressor is a machine designed to take in ordinary air from the surrounding environment and compress it into a much smaller space. This significantly increases the pressure of the air, creating a powerful source of energy for various applications.
Imagine squeezing air into a smaller balloon. That's the basic principle behind air compressors! The compressed air becomes a versatile tool, used to power everything from nail guns and paint sprayers to industrial machinery.
Types of Air Compressors
Compressed air is a powerful and versatile energy source used in various industries and home projects. But with so many different types of equipment available, choosing the right tool can be confusing. Let's break down some common compressed air tools in simple terms:
1.Reciprocating Air Compressor
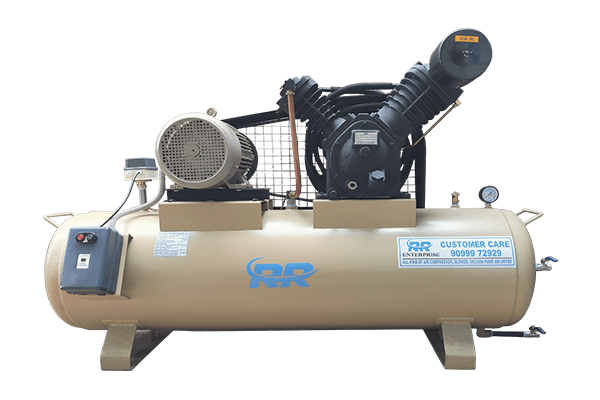

Imagine a miniature engine with a piston moving back and forth inside a cylinder. That's essentially how a reciprocating air compressor works! As the piston moves, it sucks in air and compresses it into a smaller space, increasing its pressure. Think of it like squeezing air into a smaller balloon.
- How it works: Think of a bicycle pump. As the handle moves up and down, the air gets squeezed into a smaller space, increasing pressure. Reciprocating compressors work the same way, but with a motor driving the piston.
- Where to use: These are popular due to their affordability and portability. They're perfect for inflating tyres, powering nail guns and paint sprayers, or smaller workshop tasks.
Pros:
- Affordable and portable, making them ideal for home workshops and DIY projects.
- Easy to maintain.
Cons:
- Can be noisy due to the piston movement.
- Limited airflow, not suitable for continuous industrial use.
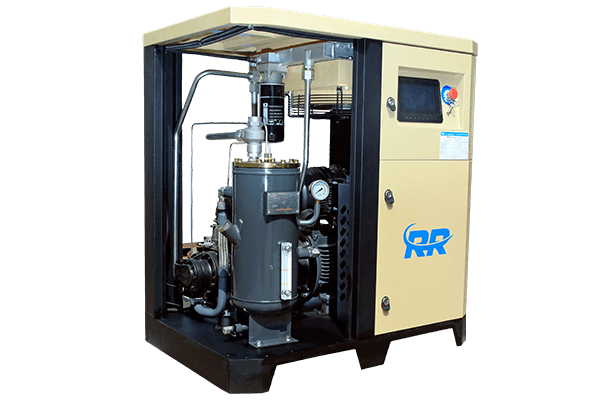
2. Rotary Screw Air Compressor
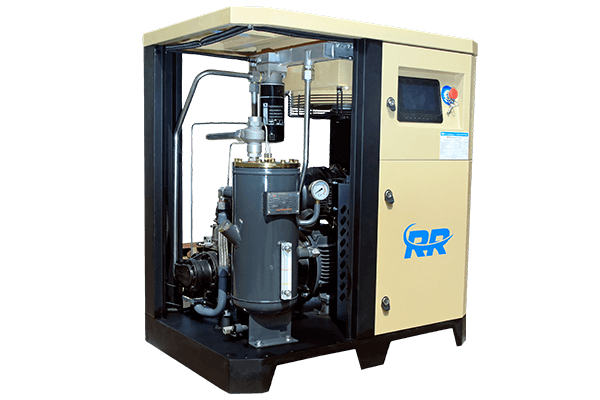

Imagine two intermeshing screws constantly turning inside a chamber. This is the heart of a rotary screw air compressor. As the screws rotate, they trap air and compress it continuously without the need for pistons. Think of it as a continuous flow of air being squeezed by the screws.
- How it works: Imagine gears constantly turning and pushing air between them. As the screws rotate, air gets trapped and squeezed into a smaller space, resulting in continuous high-pressure air.
- Where to use: These are ideal for industrial applications requiring continuous high pressure, like powering machinery in factories or large construction sites. They're quieter and more efficient than reciprocating compressors, but they have a larger footprint and a higher cost.
Pros:
- Quieter operation compared to reciprocating compressors.
- More efficient due to continuous operation.
- Delivers a constant flow of compressed air, ideal for industrial applications.
Cons:
- Larger footprint and higher initial cost compared to reciprocating compressors.
After these 2 types, we will see the specialized tools, ensuring you have a comprehensive understanding of the compressed air ecosystem.
- Blowers
- Vacuum Pumps
- Boosters
- Air Dryers
Blowers:-
move gas but don't necessarily increase its pressure significantly.
Twin Lobe Roots Blower
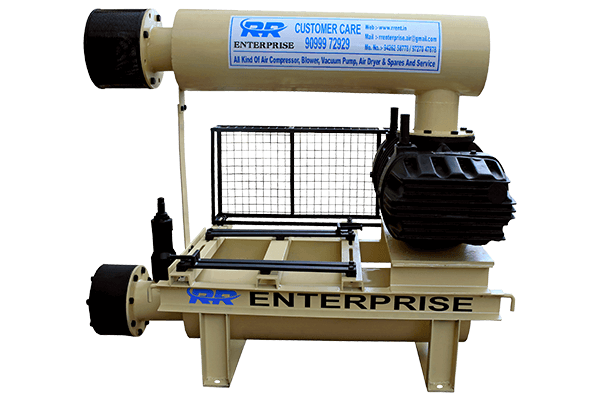
These specialized compressors focus on moving large volumes of air at a lower pressure. Imagine a pair of interlocking lobes rotating inside a chamber, pushing air through the system. They operate oil-free, suitable for specific industries with cleanliness requirements.
- How it works: The lobes rotate without actually compressing the air trapped between them. Instead, they efficiently move large volumes of air at lower pressure.
- Where to use: These are perfect for applications requiring high airflow, like pneumatic conveying systems that transport materials like grain or pellets through tubes.
Pros:
- Delivers high-volume air at lower pressure, ideal for pneumatic conveying systems used to transport materials like grain or pellets.
- The oil-free operation makes them suitable for industries dealing with sensitive materials.
Cons:
- Not designed for high-pressure applications.
Vacuum pumps:-
decrease the pressure of a gas, creating a vacuum.
Reciprocating Dry Vacuum Pump
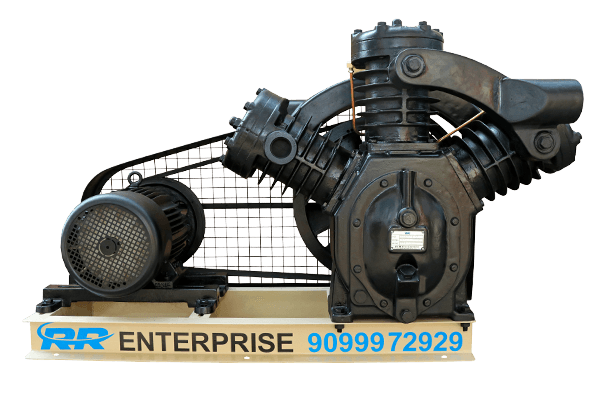
Think of a reciprocating air compressor in reverse! This pump uses a piston to create a vacuum (low pressure) instead of compressing air. Imagine a piston pulling air out of a container, creating an empty space.
- How it works: The piston movement creates a low-pressure zone, "sucking" in air or gases from a container. This creates a vacuum for various applications.
- Where to use: These are essential for removing contaminants, moisture, or air from systems. They're used in tasks like degassing liquids, maintaining vacuum chambers in laboratories, or packaging processes.
Pros:
- Ideal for removing dust, contaminants, or moisture from a system.
- Relatively simple and affordable compared to other vacuum pumps.
Cons:
- Limited vacuum level compared to some other options.
Boosters:-
further increase the pressure of an already compressed gas.
1.Vacuum Booster
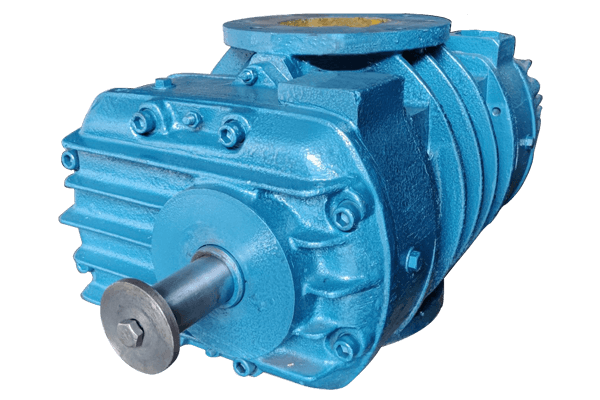

Imagine giving your existing vacuum pump a boost! A vacuum booster piggybacks on an existing pump, further reducing the pressure to even lower levels. Think of it as a supercharger for vacuum pumps.
- How it works: Connected to a regular vacuum pump, the booster further reduces the pressure by creating an additional "sucking" stage.
- Where to use: These are used in specialized industrial processes requiring ultra-low pressure environments, like freeze drying or high-vacuum chambers for scientific research.
Pros:
- Achieves ultra-low pressure levels beyond the capabilities of a standard vacuum pump.
Cons:
- Adds complexity and cost to the vacuum system.
2.High-Pressure Air Booster
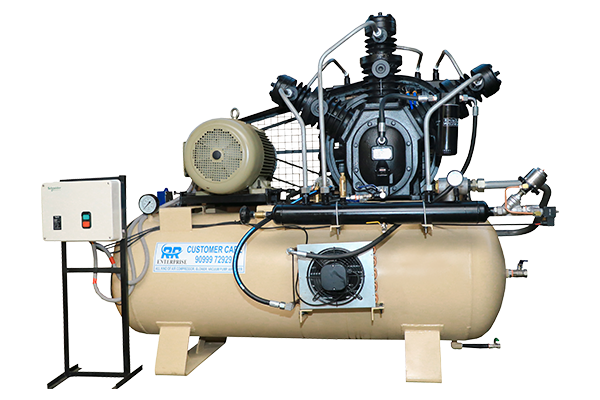
Sometimes, you need an extra punch of compressed air power. A high-pressure air booster takes existing compressed air and increases its pressure even further. Imagine taking a bottle of compressed air and squeezing it even tighter!
- How it works: Air flows through the booster, encountering valves and chambers that further increase its pressure.
- Where to use: These are ideal for applications requiring high-force bursts, like powering heavy-duty pneumatic tools or conducting pressure testing on equipment.
Pros:
- Provides an extra burst of high-pressure air for specific applications.
Cons:
- Requires a source of already compressed air to function.
Air Dryers:-
remove moisture from compressed air.
2.Refrigeration-Type Air Dryer
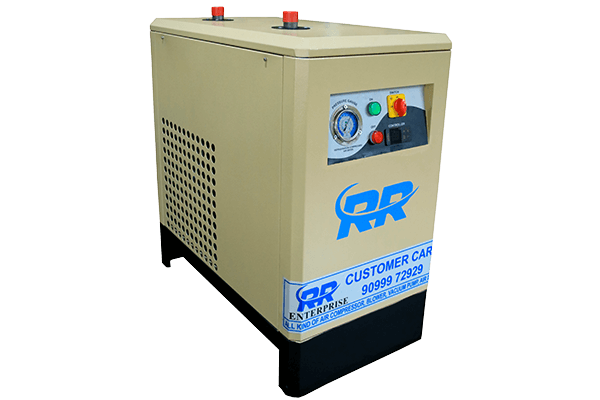

Moisture in compressed air systems can be a hidden enemy, causing corrosion and equipment damage. A refrigeration-type air dryer acts as a dehumidifier for compressed air. Imagine removing moisture from the air by chilling it, similar to how condensation forms on a cold glass.
- How it works: Similar to a refrigerator, it uses cool temperatures to condense moisture out of the air, ensuring clean and dry compressed air for your tools and equipment.
- Where to use: These are essential for any system using compressed air, especially in applications where moisture can be detrimental, like painting, food processing, or pharmaceutical industries.
Pros:
- It removes moisture from compressed air systems, preventing corrosion and equipment damage.
- Essential for applications where clean, dry air is critical.
Cons:
- Adds complexity and cost to the compressed air system
Conclusion
Understanding air compressors and their related equipment can seem complex, but with this knowledge, you're well on your way to choosing the right equipment for your needs. Whether you're a DIY enthusiast or an industrial professional, learning about compressed air systems can give you the confidence to tackle your tasks successfully.
At RR Enterprises, Vapi's leading air compressor provider and manufacturer, our expert team is always happy to help you navigate your specific needs and find the perfect air compressor or vacuum solution for your workshop or facility. Feel free to Contact Us for any assistance, as we are always ready to serve you.











